Table of Contents

Calculate Aluminum Cable Size
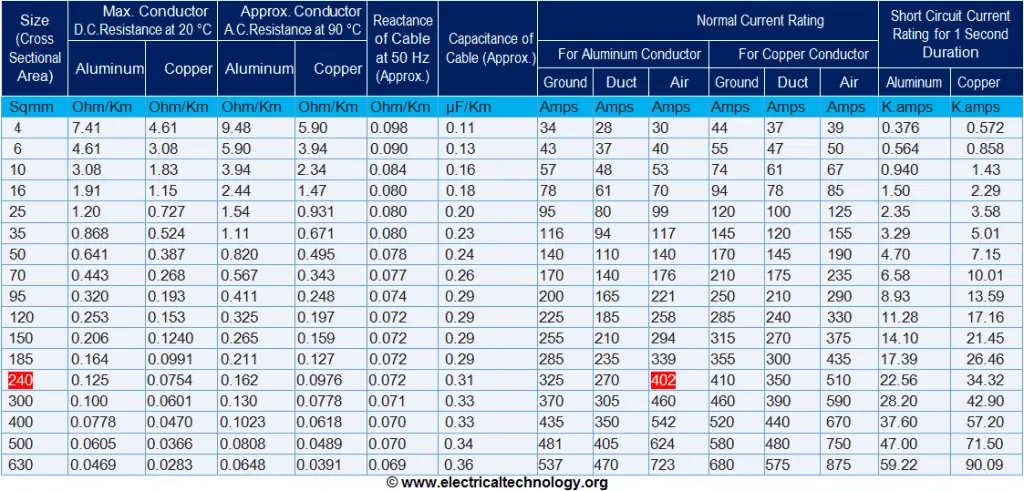
To calculate the aluminum cable size needed for a transformer, you need to first determine the current draw of the transformer, then use the formula: Cable size (mm²) = (Current (A) * Distance (m) * Correction factor) / (Voltage drop allowed (V) * Resistivity of aluminum (Ω/m/mm²)); where the correction factor accounts for factors like ambient temperature and cable type, and the resistivity of aluminum is a constant value you can find in electrical tables.
Key steps:
- Find the transformer current:
- Use the transformer rating (kVA) and the system voltage to calculate the full load current (FLA) using the formula: FLA (A) = (kVA * 1000) / (√3 * Voltage (V)).
- Determine the cable length:
- Measure the distance from the transformer to the load point (one way) and double it to get the total cable length.
- Choose an acceptable voltage drop:
- Consult electrical codes or standards to determine the maximum acceptable voltage drop percentage for your application.
- Select a correction factor:
- Based on the cable type, ambient temperature, and installation method, use a correction factor from electrical tables.
- Look up the resistivity of aluminum:
- Find the resistivity of aluminum in Ω/m/mm² from a reference table.
- Apply the formula:
- Plug the calculated current, cable length, correction factor, voltage drop, and resistivity of aluminum into the formula to get the required cable size in mm².
Important considerations:
Consider the safety factor: When selecting a cable size, it’s often recommended to choose a slightly larger size than the calculated minimum to account for potential future load increases or other uncertainties.
Always consult electrical codes and standards:Ensure the chosen cable size meets the requirements of your local electrical codes.
Use a cable size calculator:Many online calculators can simplify the process of cable sizing by inputting the relevant parameters.
Calculate Copper Cable Size➕
To calculate the copper cable size needed for a transformer, you need to first determine the full load current (FLA) of the transformer, then use the formula: Cable size (mm²) = (FLA x 1.5) / Cable Current Carrying Capacity (A), where the “cable current carrying capacity” is a value found in cable manufacturer specifications based on the cable size and type; always consider factors like voltage drop and derating factors when selecting the final cable size.
Key steps:
- Find the transformer’s full load current (FLA):This information is usually found on the transformer nameplate. If not, you can calculate it using the formula: FLA = (Transformer Power (kVA) / (√3 x Line Voltage)).
- Select a suitable cable type:Consider factors like insulation type, operating temperature, and environmental conditions when choosing the copper cable.
- Consult cable manufacturer data:Find the current carrying capacity of different cable sizes for your chosen cable type.
- Apply derating factors:Depending on the installation conditions (like ambient temperature, cable bundling), you may need to reduce the cable’s current carrying capacity using derating factors.
Important considerations:
- Voltage drop: Ensure the calculated cable size results in an acceptable voltage drop at the load point, usually within a specified percentage. From Energy meter to Distribution board, Voltage From Energy meter to Distribution board, Voltage drop should be 1.25% and for final sub circuit, vol op should be 1.25% and for final sub circuit, voltage drop should not tage drop should not
- exceed 2.5% of Supply voltage.
- Short circuit current:For high power transformers, consider the potential short circuit current and select a cable that can handle it safely.
- Safety margin:It’s generally recommended to select a slightly larger cable size than the minimum calculated value to account for potential future load increases.

Detailed Form⬇️
You can Also Use Cable Size Calculator
-Voltmen Energy Solutions PVT LTD
To Visit our store press the button above
Sign In With Google From the button Given Bellow⬇️


